Homework_1
基础概念
解释游戏对象(GameObjects)和资源(Assets)的区别与联系。
- 区别
- 游戏对象(GameObjects)
游戏中的每一个对象都是一个游戏对象。他们本身不会做任何事情,我们赋予他们各自的属性之后,就成为了我们在游戏中看到的角色或环境等。
可以将游戏对象比喻成一个空容器,再向其加入其中的组件和赋予其的属性后,它变得与其他游戏对象不同
- 资源(Assets)
资源有很多,比如对象、材质、场景、声音、预设、贴图、脚本和动作资源。这些资源可以在项目打开时,被导入到游戏里。可以被游戏对象使用,也可以被实例化为游戏对象。
- 游戏对象(GameObjects)
- 联系
资源被导入到游戏中,与游戏对象相互配合以此完成相应功能。
- 区别
编写一个代码,使用 debug 语句来验证 MonoBehaviour 基本行为或事件触发的条件
- 基本行为包括 Awake() Start() Update() FixedUpdate() LateUpdate()
常用事件包括 OnGUI() OnDisable() OnEnable()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54public class NewBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour {
// 限制 update 的输出次数
private int UpdateTest;
private int OnGuiTest;
private int FixedUpdateTest;
private int LateUpdateTest;
void Start () {
UpdateTest = FixedUpdateTest = 0;
OnGuiTest = LateUpdateTest = 0;
Debug.Log("Start");
}
void Update () {
if (UpdateTest != 3) {
Debug.Log("Update");
UpdateTest += 1;
}
}
private void Awake() {
Debug.Log("Awake");
}
private void FixedUpdate() {
if (FixedUpdateTest != 3) {
Debug.Log("FixedUpdate");
FixedUpdateTest += 1;
}
}
private void LateUpdate() {
if (LateUpdateTest != 3)
{
Debug.Log("LateUpdate");
LateUpdateTest += 1;
}
}
private void OnGUI() {
if (OnGuiTest != 3) {
Debug.Log("OnGUI");
OnGuiTest += 1;
}
}
private void OnDisable() {
Debug.Log("OnDisable");
}
private void OnEnable() {
Debug.Log("OnEnable");
}
}
查找脚本手册,了解 GameObject,Transform,Component 对象
分别翻译官方对三个对象的描述(Description)
- GameObject
- GameObjects are the fundamental objects in Unity that represent characters, props and scenery.
- 游戏对象是在 Unity 中代表任务,道具和场景的基础对象
- Transform
- The Transform component determines the Position, Rotation, and Scale of each object in the scene.
- 变化组件决定了场景中游戏对象的位置,大小和旋转关系。
- Component
- Components are the nuts & bolts of objects and behaviors in a game.
- 组件是游戏对象和其对应行为之间的枢纽。
- GameObject
描述下图中 table 对象(实体)的属性、table 的 Transform 的属性、 table 的部件
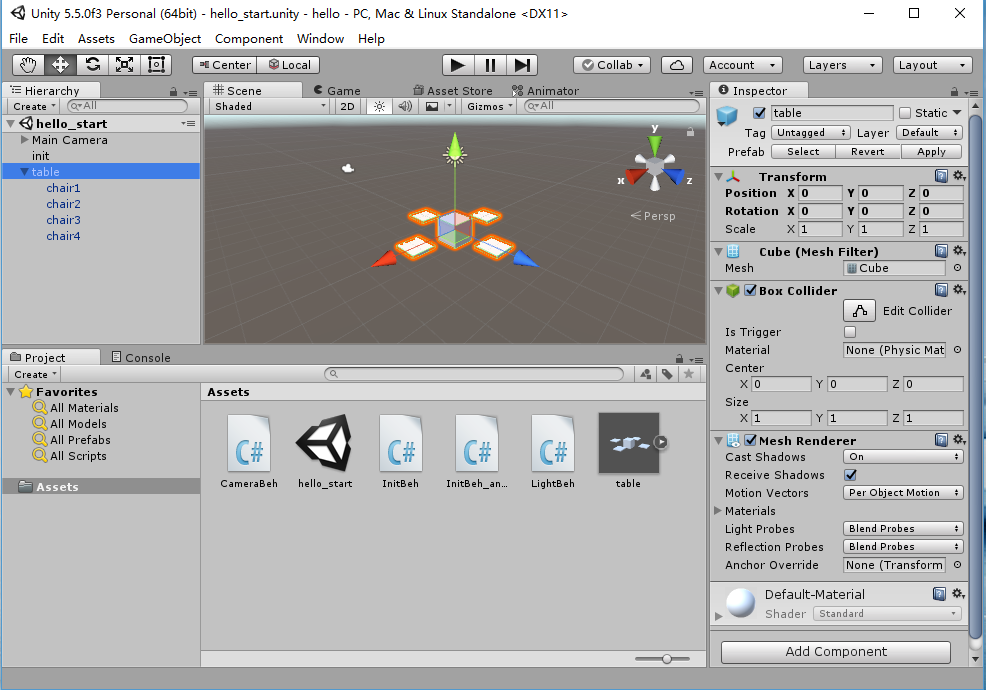
table 对象(实体)的属性
- layer : Default
- tag : Untagged
table 的 Transform 的属性
- Position: (0, 0, 0)
- Rotation: (0, 0, 0)
- Scale : (1, 1, 1)
table 的 部件
- Transform
- Mesh Renderer
- Box Collider
用 UML 图描述 三者的关系(请使用 UMLet 14.1.1 stand-alone版本出图)

整理相关学习资料,编写简单代码验证以下技术的实现:
查找对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12//Finds a GameObject by name and returns it.
GameObject.Find("Name");
//Return a list of active GameObjects tagged tag.
//Return empty array if no GameObject was found.
GameObject.FindGameObjectsWithTag("TagName");
//Return one active GameObject tagged tag.
//Returns null if no GameObject was found.
GameObject.FindWithTag("TagName");
//Return the first active loaded object of Type type.
GameObject.FindObjectOfType("TypeName");
//Return a list of all active loaded objects of Type type.
GameObject.FindObjectsOfType("TypeName");添加子对象
1
GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType);
遍历对象树
1
2
3foreach(Transform child in transform) {
//do something here
}清除所有子对象
1
2
3foreach(Transform child in transform) {
Destroy(child.gameObject);
}
预设与克隆
- 预设(Prefabs)有什么好处?与对象克隆 (clone or copy or Instantiate of Unity Object) 关系?
预设是一种资源。向场景添加一个预设时,就会创建它的一个实例。所以预设可以看作游戏对象的模板。当对预设作出任何更改时,这些更改将应用于所有与之链接的实例。
对象克隆,就是 clone 或者 copy 了一个原本对象的实例,二者之间没有相互影响。
- 制作 table 预制,写一段代码将 table 预制资源实例化成游戏对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class NewBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour {
private string prePath = "prefabs/table";
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
GameObject Table =
Instantiate(Resource.Load(prePath), new Vector(4, 0, 0), Quaternion.identity) as GameObject;
}
}
- 预设(Prefabs)有什么好处?与对象克隆 (clone or copy or Instantiate of Unity Object) 关系?
尝试解释组合模式(Composite Pattern / 一种设计模式)并使用 BroadcastMessage() 方法向子对象发送消息
组合模式是将对象组合成树形结构,以表示“部分整体”的层次结构,并使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
父类对象:
1
2
3
4
5
6public class ParentBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour {
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
this.BroadcastMessage("Test");
}
}子类对象:
1
2
3
4
5public class ChildBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour {
void Test() {
Debug.Log("Child Received");
}
}
